Note
Click here to download the full example code
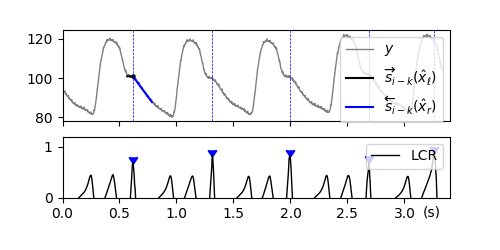
Notch Detection in ABP Signal [ex402.0]#
Example published in [Waldmann2022] as Example 2.
Arterial blood pressure (ABP) signals usually show a dicrotic notch in the decreasing slope which are considered as the end of a systolic cycle. To detect these notches, we here use a Two-Sided Line Model (TSLM).
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from scipy.signal import find_peaks
import lmlib as lm
from lmlib.utils.generator import gen_wgn, load_csv
# Linear Constraints
H_Free = np.array([[1, 0, 0, 0], # x_A,left : offset of left line
[0, 1, 0, 0], # x_B,left : slope of left line
[0, 0, 1, 0], # x_A,right : offset of right line
[0, 0, 0, 1]]) # x_B,right : slope of right line
H_Continuous = np.array(
[[1, 0, 0], # x_A,left : offset of left line
[0, 1, 0], # x_B,left : slope of left line
[1, 0, 0], # x_A,right : offset of right line
[0, 0, 1]]) # x_B,right : slope of right line
H_Straight = np.array(
[[1, 0], # x_A,left : offset of left line
[0, 1], # x_B,left : slope of left line
[1, 0], # x_A,right : offset of right line
[0, 1]]) # x_B,right : slope of right line
H_Horizontal = np.array(
[[1], # x_A,left : offset of left line
[0], # x_B,left : slope of left line
[1], # x_A,right : offset of right line
[0]]) # x_B,right : slope of right line
H_Left_Horizontal = np.array(
[[1, 0], # x_A,left : offset of left line
[0, 0], # x_B,left : slope of left line
[1, 0], # x_A,right : offset of right line
[0, 1]]) # x_B,right : slope of right line
H_Right_Horizontal = np.array(
[[1, 0], # x_A,left : offset of left line
[0, 1], # x_B,left : slope of left line
[1, 0], # x_A,right : offset of right line
[0, 0]]) # x_B,right : slope of right line
H_Peak = np.array([[1, 0], # x_A,left : offset of left line
[0, 1], # x_B,left : slope of left line
[1, 0], # x_A,right : offset of right line
[0, -1]]) # x_B,right : slope of right line
H_Step = np.array([[1, 0], # x_A,left : offset of left line
[0, 0], # x_B,left : slope of left line
[0, 1], # x_A,right : offset of right line
[0, 0]]) # x_B,right : slope of right line
# Implementation of Two-Sided Line Model (TSLM)
# y: input signal vector
# a,b: left and right sided interval border (in number of samples)
# gl, gr: left and right sided exponential window weight (defines exponential decay factor gamma)
def J_TSLM(y, a, b, gl, gr):
# Set up Composite Cost Model using two ALSSMs and exponentially decaying windows
#
# ----> <----
# --------------------
# A_L | c_L | 0 |
# --------------------
# A_R | 0 | c_R |
# --------------------
# : : :
# a=-80 0 b=20
alssm_left = lm.AlssmPoly(poly_degree=1) # A_L, c_L
alssm_right = lm.AlssmPoly(poly_degree=1) # A_R, c_R
segment_left = lm.Segment(a=a, b=-1, direction=lm.FORWARD, g=gl)
segment_right = lm.Segment(a=0, b=b, direction=lm.BACKWARD, g=gr)
F = [[1, 0], [0, 1]] # mixing matrix, turning on and off models per segment (1=on, 0=off)
costs = lm.CompositeCost((alssm_left, alssm_right), (segment_left, segment_right), F)
return costs
# Constants
K = 2000 # number of samples
sigma = 0.015 # Adding Gaussian Noise
fs = 600 # Sampling Frequency [Hz]
k = range(K)
# -- TEST SIGNAL --
y = load_csv('cerebral-vasoreg-diabetes-heaad-up-tilt_day1-s0030DA-noheader.csv', K, channel=3) # probably sampled at 600Hz
y = y + gen_wgn(K, sigma, seed=233453) # Add Gaussian Noise
# 1 -- Onset Detection with Two-Sided Line Model (TSLM) -----
costs = J_TSLM(y, -30, 100, gl=180, gr=180)
# Filter
separam = lm.RLSAlssm(costs)
separam.filter(y)
# constraint minimization
x_hat_H1 = separam.minimize_x(H_Left_Horizontal)
x_hat_H0 = separam.minimize_x(H_Straight)
y=y[k]
x_hat_H1=x_hat_H1[k]
x_hat_H0=x_hat_H0[k]
# Square Error and LCR
error_H1 = separam.eval_errors(x_hat_H1)
error_H0 = separam.eval_errors(x_hat_H0)
lcr = -1 / 2 * np.log(np.divide(error_H1, error_H0))
# Find LCR peaks with minimal distance and height
peaks_1, _ = find_peaks(lcr, height=0.5, distance=300)
# Evaluate trajectories (for plotting only)
trajs_edge = lm.map_trajectories(costs.trajectories(x_hat_H1[peaks_1]), peaks_1, K, merge_ks=False)
trajs_line = lm.map_trajectories(costs.trajectories(x_hat_H0[peaks_1]), peaks_1, K, merge_ks=False)
wins = lm.map_windows(costs.windows(segment_indices=[1, 1]), peaks_1, K, merge_ks=True)
# -- PLOTTING --
_, axs = plt.subplots(2, 1, figsize=(5, 2.5), gridspec_kw={'height_ratios': [1.5, 1]}, sharex='all')
nax = 0
t = np.array(list(k))/fs
axs[nax].plot(t, y, lw=1.0, c='gray', label='$y$', zorder=0)
if True:
ref_index = 0
axs[nax].plot(t, trajs_edge[ref_index, 0, :], c='k', lw=1.5, ls='-', zorder=1, label='$\overrightarrow{s}_{i-k}(\hat x_\ell)$')
axs[nax].plot(t, trajs_edge[ref_index, 1, :], c='b', lw=1.5, ls='-', zorder=1, label='$\overleftarrow{s}_{i-k}(\hat x_r)$')
axs[nax].scatter(peaks_1[ref_index]/fs, x_hat_H1[peaks_1[ref_index], 0], marker='.', c='k', s=20.0)
#axs[nax].axhline(x=peaks_1, ymin=plt.ylim()[0], ymax=plt.ylim()[1])
for xp in peaks_1/fs:
axs[nax].axvline(x=xp, ls='--', c='b', lw=0.5)
#axs[nax].scatter(peaks_1, y[peaks_1], marker=7, c='b')
axs[nax].legend(loc=1)
nax+=1
axs[nax].plot(t, lcr, lw=1.0, c='k', label='LCR')
axs[nax].scatter(peaks_1/fs, lcr[peaks_1], marker=7, c='b')
axs[nax].legend(loc='upper right', labelspacing = -0.0)
axs[nax].set_ylim(-0.0, 1.2)
#axs[nax].set(xlabel='time [s]')
plt.gcf().text(0.845, 0.135, '(s)')
axs[nax].set_xlim(left=0.0, right=3.4)
plt.subplots_adjust(bottom=0.21)
plt.show()
Total running time of the script: ( 0 minutes 0.167 seconds)